US Military Spending: How It Compares & Its Priorities

The United States’ military spending significantly surpasses that of other nations, driven by a complex interplay of global strategic interests, technological superiority goals, and the sustainment of extensive defense infrastructure, with priorities frequently shifting to address emerging threats and national security objectives.
Understanding the intricacies of US Military Spending: How Does It Compare to Other Nations and What Are the Priorities? is essential for anyone seeking to grasp the economic and geopolitical landscape of the modern world. This deep dive aims to demystify the massive figures and complex considerations behind the world’s largest defense budget.
The Unparalleled Scale of US Military Spending
The sheer volume of the United States’ military budget often sparks considerable debate and draws global attention. Year after year, the figures released by organizations like the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) consistently place the U.S. at the apex of global defense spending. This dominance isn’t merely incremental; it’s a difference of magnitudes when compared to even the next largest military spenders.
Understanding the context of this spending is crucial. It’s not just about the raw numbers, but what these numbers represent in terms of global reach, technological advancement, and strategic capabilities. The U.S. budget encompasses everything from personnel salaries and healthcare to advanced weapon systems development, intelligence gathering, and global operational deployments.
Historical trends and consistent growth
Over the past few decades, despite fluctuations due to specific conflicts or economic downturns, the general trend in US military spending has been one of consistent, albeit sometimes uneven, growth. Post-Cold War reductions were relatively short-lived, with significant upticks following events like the 9/11 attacks and subsequent wars in Afghanistan and Iraq. More recently, geopolitical shifts and competition with powerful state actors have further solidified a commitment to robust defense budgets.
- Post-Cold War “peace dividend” period saw temporary declines.
- Significant increases occurred in response to the Global War on Terror.
- Ongoing modernization efforts drive sustained high expenditure levels.
The consistent growth underscores a sustained national commitment to maintaining military superiority, adapting to evolving threats, and fulfilling global security obligations that are often expected from a world superpower. This commitment is reflected in legislative efforts and appropriations that consistently allocate substantial resources to defense, irrespective of the political party in power, indicating a broad consensus on its necessity.
Examining these trends also reveals insights into policy shifts and perceived threats. For instance, the pivot towards “great power competition” in recent years has seen a renewed focus on naval power, long-range conventional capabilities, and advanced deterrence strategies, all of which are capital-intensive undertakings. These underlying strategic objectives are key drivers behind the continued scale of spending.
Factors contributing to high expenditure
Many complex factors contribute to the high level of U.S. military expenditure. Beyond the need to maintain a global military presence and respond to crises, there are fundamental structural elements. Research and development (R&D) in defense is incredibly costly, yet essential for maintaining a qualitative edge. The U.S. invests heavily in developing cutting-edge technologies, from stealth aircraft to advanced cyber warfare capabilities, ensuring its forces remain at the forefront of military innovation.
- Extensive global network of military bases and forward deployed personnel.
- Commitment to technological superiority and next-generation weapon systems.
- High personnel costs, including salaries, healthcare, and benefits for an all-volunteer force.
The extensive global network of military bases and alliances also demands significant financial resources for maintenance, logistics, and personnel support. These bases are not just strategic outposts; they are complex ecosystems requiring substantial investment. Furthermore, the U.S. operates an all-volunteer military, which necessitates competitive salaries, comprehensive healthcare, and robust benefits packages to attract and retain highly skilled personnel. These human capital costs form a substantial portion of the overall budget, often overlooked when only focusing on weapon systems. The sheer complexity of modern military operations, requiring sophisticated logistics, intelligence, and training, further inflates costs, making the “unparalleled scale” a result of multifaceted demands.
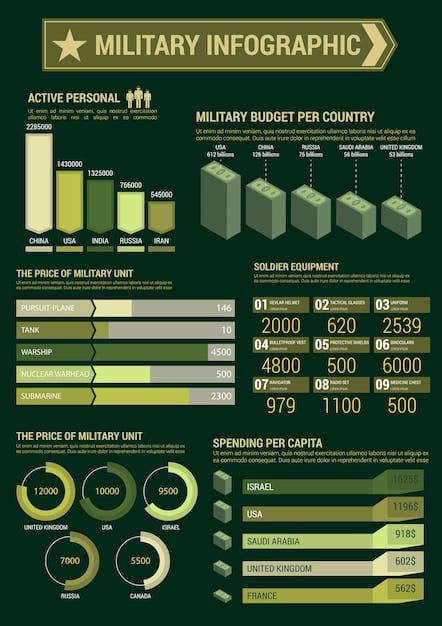
Comparing US Military Spending to Other Global Powers
When analyzing the United States’ military expenditure, its comparison to other major global powers offers a stark perspective on its scale. While several nations possess formidable militaries and allocate significant resources to defense, none approach the financial outlay of the U.S. This disparity highlights not only a difference in strategic priorities but also in economic capacities.
Typically, the next closest spenders are China, Russia, India, and Saudi Arabia, but even combined, their budgets frequently struggle to match or even come close to the U.S. figure. This financial muscle allows the U.S. to maintain capabilities that others simply cannot afford on the same scale, impacting global power dynamics and strategic calculations. It’s a key component of its diplomatic and deterrent posture.
China’s rising defense budget
China stands as the second-largest military spender globally, and its budget has been on a consistent upward trajectory for decades, mirroring its economic expansion and geopolitical ambitions. Beijing’s focus is largely on modernizing its forces, particularly its navy and air force, to extend its reach in the Indo-Pacific and beyond, challenging perceived U.S. dominance in the region. Their spending prioritizes indigenous technological development and infrastructure expansion, aimed at reducing reliance on foreign suppliers and bolstering self-sufficiency.
- Focus on naval expansion (aircraft carriers, advanced destroyers).
- Significant investment in advanced air capabilities, including stealth fighters.
- Development of cyber warfare and space-based military assets.
While impressive, China’s official military budget is widely believed to be an underestimate, with many analysts suggesting that substantial hidden costs are not publicly disclosed. Even with these caveats, the gap between China and the U.S. remains substantial, though China’s rapid growth indicates a long-term strategic intent to narrow this disparity. The modernization efforts also include a strong emphasis on capabilities designed to deter or counter U.S. military projection in areas considered vital to Chinese national interests, such as Taiwan and the South China Sea. This sustained investment represents a fundamental shift in the global military balance, creating a more multipolar defense landscape.
Russia and other major spenders
Russia, despite its reputation as a major military power, holds a significantly smaller defense budget compared to both the U.S. and China. Its spending priorities often revolve around modernizing its nuclear triad, rebuilding conventional forces after the post-Soviet decline, and investing in advanced weaponry such as hypersonics and electronic warfare systems. However, its economic limitations mean that its military’s overall size and technological breadth cannot match that of the U.S.
- Modernization of nuclear deterrent forces.
- Investment in advanced missile systems and air defenses.
- Efforts to upgrade ground forces and tactical airpower.
Other significant military spenders include India, which is rapidly modernizing its armed forces to address regional security challenges and maintain deterrence against its neighbors. Saudi Arabia and other Middle Eastern nations also rank high, driven by regional conflicts, geopolitical instability, and a desire for advanced Western military technology. European NATO members, while collectively substantial, individually spend far less than the U.S., relying heavily on American capabilities for collective defense. This diverse landscape of spending reflects varied national security imperatives, economic capacities, and geopolitical roles, all situated beneath the overarching shadow of U.S. military financial might.
Key Priorities in US Defense Spending
Beyond the sheer volume, understanding the specific priorities within the U.S. military budget provides critical insights into American defense strategy. The allocation of funds reflects not just current operational needs but also long-term strategic goals and perceived future threats. These priorities are dynamic, evolving in response to geopolitical shifts, technological advancements, and domestic political considerations affecting defense policy.
Current priorities often center on maintaining a technological edge, deterring peer competitors, and ensuring readiness for a spectrum of conflicts, from high-intensity warfare to counter-terrorism operations. This multifaceted approach requires investments across numerous domains, from air and naval superiority to cyber capabilities and space defense, reflecting a holistic view of national security in the 21st century.
Technological superiority and modernization
A cornerstone of U.S. defense strategy is the unwavering commitment to maintaining technological superiority. This involves massive investments in research, development, test, and evaluation (RDT&E) of next-generation weapon systems and capabilities. Areas such as artificial intelligence, quantum computing, hypersonics, and advanced stealth technologies receive substantial funding, aimed at ensuring the U.S. military can outmatch any adversary in future conflicts.
- Development of advanced stealth aircraft (e.g., F-35 program).
- Investment in hypersonics and directed energy weapons.
- Expansion of cyber warfare and information operations capabilities.
Modernization efforts extend beyond new weapons to upgrading existing platforms, improving network infrastructure, and enhancing command and control systems. This ensures that the current force remains relevant and effective against evolving threats, integrating cutting-edge technology into established operational structures. The rapid pace of technological change means that this is an ongoing, rather than a one-time, investment, continuously demanding significant portions of the defense budget. The goal is not merely to keep pace but to set the pace, creating asymmetric advantages that deter aggression and ensure operational success. This dedication to innovation is a fundamental distinguishing feature of U.S. defense expenditure, influencing procurement cycles and strategic planning across all branches of service, shaping the future of global warfare.
Personnel, readiness, and global presence
While advanced technology grabs headlines, a substantial portion of the U.S. defense budget is dedicated to personnel costs and ensuring military readiness. As an all-volunteer force, attracting and retaining top talent requires competitive salaries, comprehensive healthcare, housing, and educational benefits. These costs are significant but deemed essential for maintaining a highly skilled and motivated fighting force. Readiness involves rigorous training, maintenance of equipment, and sufficient supplies to ensure units can deploy and operate effectively anywhere in the world at a moment’s notice.
- Compensation and benefits for active-duty and reserve personnel.
- Extensive training exercises and operational deployments.
- Maintenance and upgrade of critical infrastructure and logistics.
The commitment to a global presence is another major financial driver. The U.S. maintains military bases and personnel in numerous countries, supporting alliances, deterring aggression, and quickly responding to international crises. These forward-deployed forces require continuous logistical support, including transportation, supplies, and infrastructure maintenance, all of which contribute heavily to the overall budget. This presence is a key pillar of U.S. foreign policy, enabling rapid projection of power and influence, and providing a robust deterrent capacity. Balancing these elements—personnel, readiness, and global reach—is a constant challenge, necessitating careful budgetary allocations that address immediate needs while preparing for future eventualities. The strength and morale of the individual soldier, sailor, airman, or marine are recognized as fundamental assets, hence the significant investment in their well-being and professional development.

The Economic and Geopolitical Implications of US Funding
The vast expenditure on the U.S. military carries profound economic and geopolitical implications, both domestically and internationally. Economically, it represents a substantial segment of the federal budget, influencing everything from national debt to job creation in the defense industry. Geopolitically, it underpins alliances, shapes international relations, and dictates the balance of power on a global scale.
Domestically, the defense industry is a significant employer and a driver of innovation, particularly in high-tech sectors. However, critics often point to the opportunity costs, arguing that such funds could be reallocated to other areas like infrastructure, education, or healthcare. Internationally, the U.S. military budget is both a source of reassurance for allies and a point of concern for potential adversaries, influencing their own defense spending and strategic postures.
Impact on domestic economy and innovation
Within the United States, military spending has a substantial, multifaceted impact on the domestic economy. The defense industry, comprising major corporations and myriad smaller suppliers, creates millions of jobs, from engineers and scientists to manufacturing workers. These jobs are often high-tech and high-wage, contributing significantly to local and regional economies, especially in states with a strong military presence or defense contractors. The investment in research and development for military applications also frequently spawns dual-use technologies that later find commercial applications, driving innovation and benefiting the broader economy.
- Job creation in defense manufacturing and technology sectors.
- Spinoff civilian technologies from military R&D (e.g., GPS, internet precursors).
- Regional economic boosts in areas with military bases or defense contractors.
However, the economic impact is not uniformly positive. Critics argue that diverting such a large portion of federal spending to defense constitutes an opportunity cost, meaning resources that could be used for other public goods are instead channeled into the military. There are debates about whether military spending truly generates as many jobs or as much economic benefit as equivalent investments in other sectors like green energy or education. Nevertheless, the defense budget remains a powerful economic engine, deeply intertwined with the nation’s industrial base and technological landscape, exerting a significant influence over innovation cycles and employment trends. The steady demand for cutting-edge materials and systems often pushes the boundaries of manufacturing and computational science, benefiting multiple parallel industries that are indirectly supported by these military requirements.
Global power projection and alliances
The U.S. military budget’s primary geopolitical implication is its role in enabling unparalleled global power projection. The ability to deploy forces, conduct operations, and provide humanitarian aid anywhere in the world reinforces the U.S.’s status as a superpower. This capacity underpins its network of alliances, offering security guarantees to countries from Europe to Asia, fostering stability in volatile regions, and deterring potential aggressors. Allies often see U.S. military might as a crucial counterbalance to rising powers or regional threats, reducing their own need for massive expenditures on certain high-cost capabilities.
- Maintaining strategic deterrence against peer and near-peer competitors.
- Supporting international stability and responding to humanitarian crises.
- Strengthening alliances through joint exercises and security cooperation.
Conversely, this vast military spending can be perceived as aggressive or threatening by rival nations, potentially escalating arms races and creating international tensions. The strategic implications are immense: it shapes everything from arms control negotiations to trade relationships. The U.S. military’s reach means it can intervene in distant conflicts, respond to natural disasters, and enforce maritime security, acting as a global policeman in some respects, thereby influencing international norms and laws. The balance between maintaining robust capabilities for national security and avoiding the perception of belligerence is a constant challenge, reflecting the complex interplay between economic strength, military might, and diplomatic influence on the world stage. The very presence of U.S. forces often acts as a stabilizing element, preventing regional conflicts from spiraling out of control.
Challenges and Debates Surrounding Defense Spending
The enormous scale of US military spending is not without its challenges and ongoing debates. These discussions often span the spectrum from fiscal responsibility and strategic effectiveness to ethical considerations and the allocation of national resources. Understanding these challenges provides a more nuanced view of the complexities inherent in maintaining the world’s largest defense budget.
Common critiques include concerns about inefficiency, waste, and the prioritization of certain projects over others. The debate frequently pits those advocating for robust defense against those who believe resources could be better utilized elsewhere to address domestic needs or other global challenges like climate change and pandemics. These debates are often highly politicized, reflecting different national priorities and ideological stances.
Efficiency, waste, and accountability
One of the most persistent criticisms leveled against the U.S. military budget is the issue of efficiency, waste, and accountability. Reports from government watchdogs and independent analyses frequently highlight instances of cost overruns on major weapons programs, redundant contracts, and inefficient bureaucratic processes. The sheer size of the Pentagon’s budget makes oversight challenging, leading to concerns about how efficiently taxpayer money is being utilized to achieve defense objectives. The extensive network of contractors further complicates the picture, with debates often arising over profitability and transparency in the defense industrial base.
- Frequent cost overruns on major weapon system procurements.
- Challenges in auditing and tracking expenditures across vast departments.
- Concerns over the “revolving door” between the Pentagon and defense contractors.
Calls for greater accountability and transparency are common, with suggestions ranging from more rigorous auditing to re-evaluating procurement processes to incentivize cost-effectiveness. The complexity of modern military systems and the long development cycles contribute to these challenges, as unforeseen technical issues or changing requirements can significantly inflate costs. Despite efforts to streamline operations, the sheer scale and scope of the Department of Defense make it inherently difficult to eliminate all inefficiencies. The ongoing debate emphasizes the need for a balance between providing the military with necessary resources and ensuring fiscal responsibility, especially given the public’s concern over national debt and the allocation of funds amidst other pressing societal needs.
Balancing security needs with other national priorities
A fundamental debate surrounding U.S. military spending revolves around balancing perceived security needs with other pressing national priorities. Critics argue that the vast sums allocated to defense detract from investments in areas such as education, healthcare, infrastructure, and climate change mitigation. This “guns versus butter” dilemma reflects a deeper philosophical question about how a nation should best allocate its resources to ensure overall well-being and long-term prosperity.
- Calls for reallocation of funds to address domestic issues like healthcare and education.
- Debates over the economic sustainability of continually rising defense budgets.
- Discussions on the optimal balance between hard power and soft power in foreign policy.
Advocates for robust defense spending contend that national security is the paramount responsibility of government, arguing that a strong military is essential for protecting national interests, deterring adversaries, and maintaining global stability, which indirectly supports economic prosperity. They often emphasize the unpredictable nature of global threats and the need to be prepared for any eventuality. However, those
seeking cuts often point to the social and economic costs of maintaining such a large military apparatus, suggesting that some security challenges might be better addressed through diplomatic, economic, or humanitarian efforts. This ongoing tension between different national priorities is a constant feature of congressional budget debates, reflecting the complex interplay of values, perceived threats, and economic realities within American society. Ultimately, the resolution of this balance depends on evolving geopolitical circumstances and the prevailing domestic policy agenda, requiring continuous recalibration and public discourse to find an optimal equilibrium for the nation’s future.
Future Outlook for US Military Spending
Predicting the future trajectory of U.S. military spending involves navigating a complex web of domestic political dynamics, evolving global threats, and technological advancements. While the U.S. is likely to remain the top military spender for the foreseeable future, the specific priorities and the growth rate of its budget will depend on several critical factors, reflecting both continuity and potential shifts in strategic direction.
The pace of technological innovation, the actions of peer competitors, and the U.S.’s role in a changing global order will all play significant roles. Additionally, internal pressures, such as economic conditions and public sentiment, can influence congressional appropriations and executive branch policy decisions regarding defense. The outlook suggests a continuous adaptation to new challenges while maintaining core capabilities.
Responding to emerging threats and technologies
The future of U.S. military spending will be heavily shaped by its response to emerging threats and disruptive technologies. The rise of sophisticated cyber warfare capabilities, the proliferation of advanced missile systems, and the increasing reliance on space-based assets all demand significant investment to maintain defensive and offensive edges. Countering the strategic challenges posed by countries like China and Russia, particularly in areas like artificial intelligence, quantum computing, and hypersonics, will necessitate continued and substantial R&D expenditure.
- Increased investment in cybersecurity and space defense.
- Focus on developing counter-hypersonic and AI-driven military applications.
- Adaptation to hybrid warfare tactics and asymmetric threats.
Beyond traditional warfare domains, the military is increasingly recognizing and investing in capabilities to address non-traditional threats, such as climate-related security risks, global pandemics, and information warfare. These evolving landscapes require new types of military expertise, equipment, and international cooperation, which will influence budget allocations. The imperative to maintain a technological overmatch means that the defense budget will likely continue to prioritize cutting-edge research, rapid prototyping, and fielding of next-generation systems, ensuring the U.S. military remains ahead of potential adversaries in an accelerating technological race. This dynamic environment requires flexible budget processes that can quickly pivot to address novel challenges, demanding sustained commitment to innovation and strategic foresight, redefining the very nature of deterrence and defense in the modern era.
Congressional priorities and public opinion
Future U.S. military spending will also be significantly influenced by congressional priorities and the shifting tides of public opinion. While there is often bipartisan support for a strong national defense, specific budgetary allocations can become highly contentious. Different political factions may prioritize different aspects of defense, such as personnel benefits versus advanced weapons procurement, or strategic force posture versus domestic readiness, leading to annual legislative battles over the Pentagon’s budget.
- Impact of economic conditions on willingness to spend on defense.
- Influence of political shifts on strategic military priorities.
- Role of public and media perception in shaping defense debates.
Public opinion, shaped by major geopolitical events, economic prosperity (or lack thereof), and perceived threats, can exert considerable pressure on lawmakers. For instance, prolonged military engagements abroad or significant domestic economic challenges can lead to public calls for reduced defense spending, while escalating international tensions or attacks can shift sentiment towards greater investment. The balance between maintaining military strength and addressing domestic needs will remain a central theme. The advocacy of veteran groups, defense industry lobbyists, and think tanks also plays a crucial role in shaping the narrative and influencing policy discussions. Therefore, the future trajectory of U.S. military spending will not solely be determined by military strategists but also by the complex interplay of political will, economic realities, and the evolving collective priorities of the American populace, ensuring it remains a subject of continuous public and legislative debate.
| Key Aspect | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 📊 Global Comparison | The US military budget significantly dwarfs all other nations, often exceeding the next several top spenders combined. |
| 🔬 Key Priorities | Focus on technological superiority, personnel readiness, and maintaining extensive global presence. |
| 🌍 Geopolitical Impact | Funds global power projection, strengthens alliances, and influences international relations. |
| 🚧 Challenges & Future | Debates on efficiency, balancing priorities, and adapting to emerging threats and tech define its future. |
Frequently Asked Questions About US Military Spending
▼
The United States’ military spending is significantly higher than any other nation. It consistently exceeds the combined budgets of the next several highest-spending countries, including China, India, Russia, and Saudi Arabia, reflecting its unique global security commitments and technological ambitions.
▼
Key priorities include maintaining technological superiority, investing heavily in research and development for next-generation weapons, ensuring high readiness for personnel and equipment, and funding a vast global presence through military bases and alliances. Personnel costs and modernization efforts are significant components.
▼
Domestically, it creates significant employment in the defense industry, drives innovation linked to dual-use technologies, and boosts regional economies. However, it also represents a substantial portion of federal expenditure, leading to debates about opportunity costs and resource allocation versus other national priorities like healthcare or infrastructure.
▼
It enables unparalleled global power projection, strengthens its network of alliances, and acts as a deterrent to potential adversaries. This spending shapes international relations by influencing the balance of power, contributing to regional stability, and sometimes prompting other nations to increase their own defense budgets in response.
▼
Major challenges include concerns over efficiency, waste, and accountability in procurement, as well as the ethical debates around military interventions. Debates also revolve around balancing defense needs with other national priorities, the sustainability of rising budgets, and adapting to rapidly evolving threats and technologies.
Conclusion
The discussion surrounding US military spending is multifaceted, deeply entrenched in both economic realities and geopolitical necessities. As this analysis has shown, the sheer scale of the budget sets the United States apart from every other nation, reflecting a deliberate strategic choice to maintain unparalleled global military capabilities. The priorities within this colossal budget underscore a commitment to technological superiority, the readiness of its all-volunteer force, and the maintenance of a vast global presence that underpins its alliances and security commitments. While these expenditures foster innovation and project global influence, they also spark important debates concerning economic efficiency, accountability, and the perennial challenge of balancing military might with other pressing national needs. Looking forward, the future of US defense spending will undoubtedly be shaped by its response to emerging threats, the relentless pace of technological change, and the evolving interplay of domestic political will and public sentiment, ensuring it remains a central, often contentious, element of national and international discourse.





